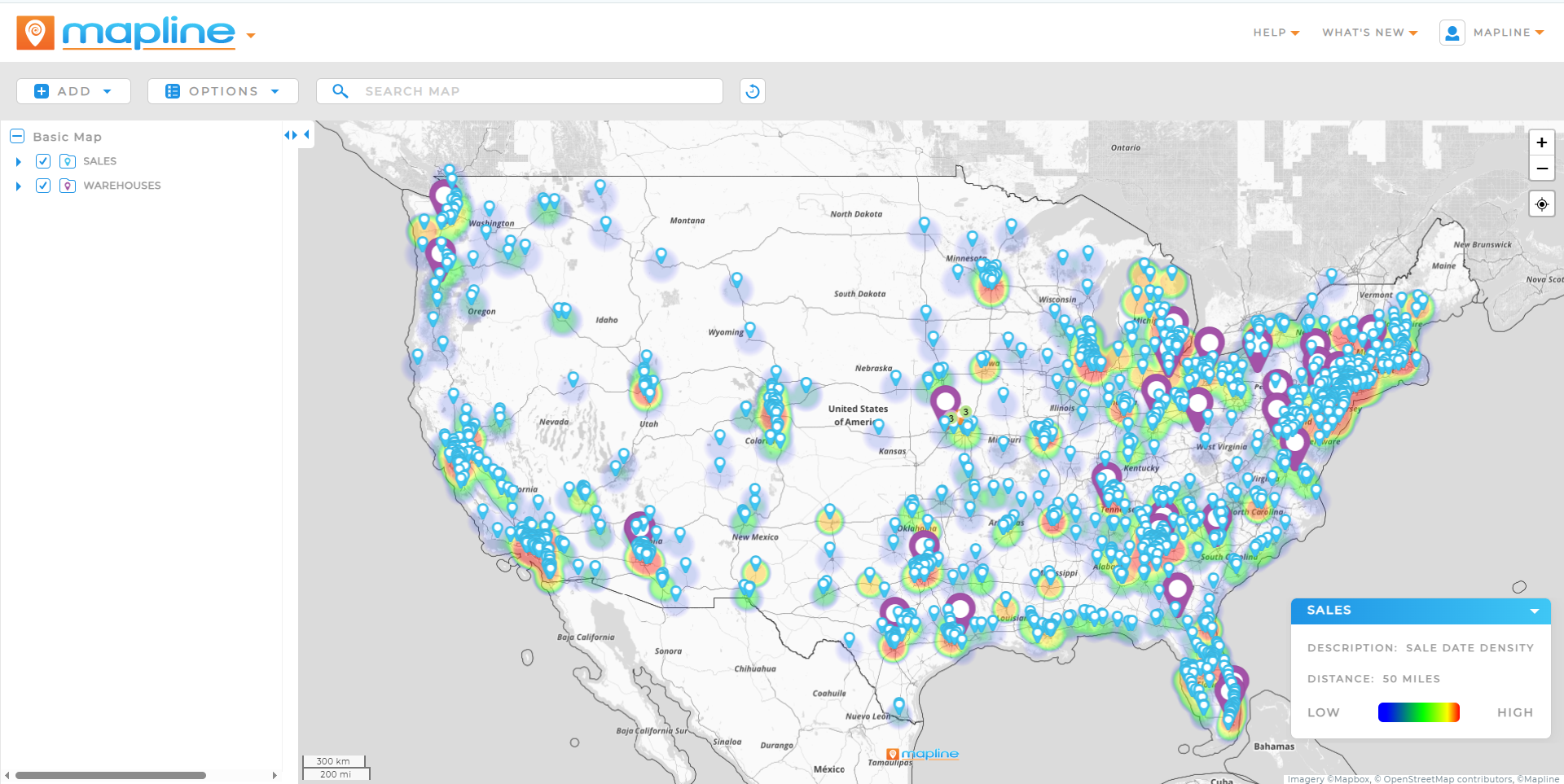
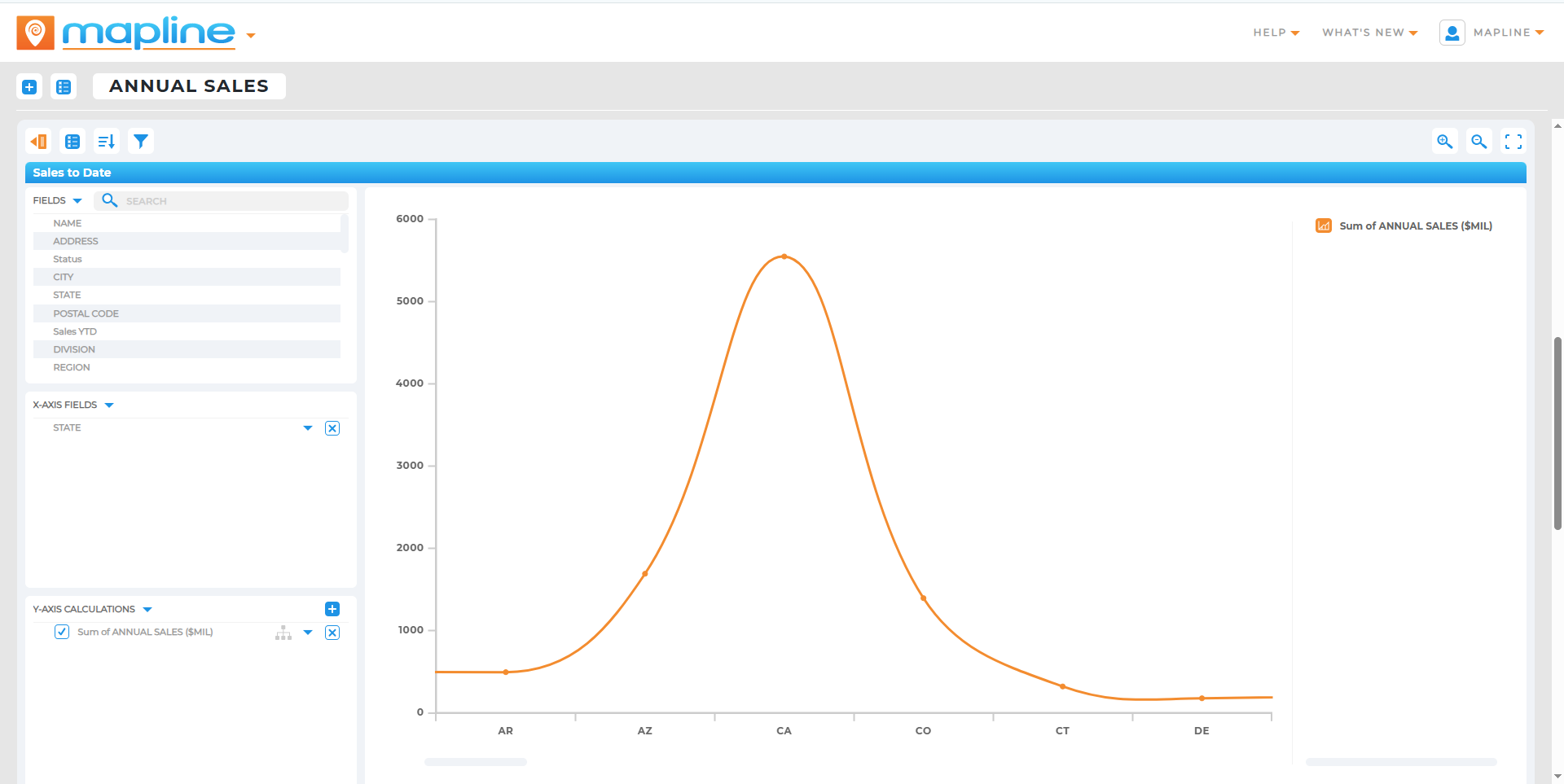
In a fast-moving, data-driven world, companies that can predict, prescribe, and act outperform those that simply report. That’s the power of advanced analytics. It turns raw data into forward-looking intelligence—using AI, machine learning, and complex models to reveal not just what happened, but what’s likely to happen next—and how to respond.
This guide explores the major categories of advanced analytics tools and how they help businesses uncover anomalies, optimize strategy, and model customer behavior at scale. From spatial AI to marketing attribution, you’ll learn how to move from hindsight to foresight with the right tech stack.
What Is Advanced Analytics?
Advanced analytics goes beyond traditional business intelligence. Rather than simply summarizing past performance, it uses statistical models, machine learning, and AI to generate predictions, detect patterns, and prescribe optimal actions.
Where basic BI answers “what happened?”, advanced analytics answers:
- What’s likely to happen? (Predictive analytics)
- What should we do? (Prescriptive analytics)
- Is anything unusual happening? (Anomaly detection)
- What patterns or relationships can we uncover? (AI and spatial modeling)
Advanced analytics platforms are essential for organizations looking to automate insight generation, reduce risk, and optimize performance across functions.
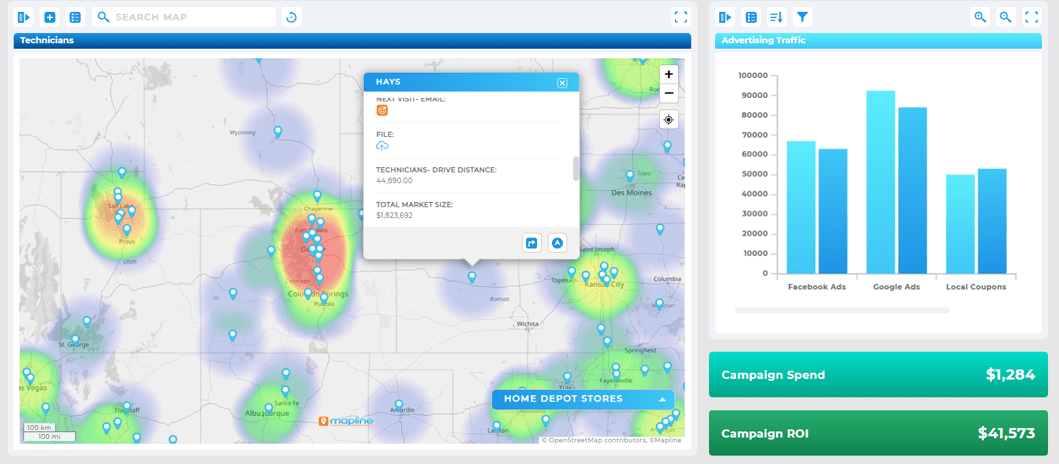

Pro Tip: Use machine learning to automate and scale your attribution models! Many teams still rely on static or rule-based attribution. By introducing machine learning analytics into your attribution strategy, you unlock automated model refinement, real-time adaptation, and deeper insights across your full funnel.
Core Toolsets for Predictive and Prescriptive Intelligence
The foundation of advanced analytics lies in its ability to forecast trends and prescribe optimal actions. These tools guide strategic and operational decision-making at every level. Predictive analytics platforms use historical data to anticipate customer behavior, market shifts, or supply chain disruptions before they happen. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further—recommending specific actions or resource allocations based on potential outcomes. Together, they help businesses reduce risk, maximize ROI, and stay agile in fast-changing environments. Whether you’re planning inventory, pricing campaigns, or field deployments, these insights turn guesswork into data-backed strategy.
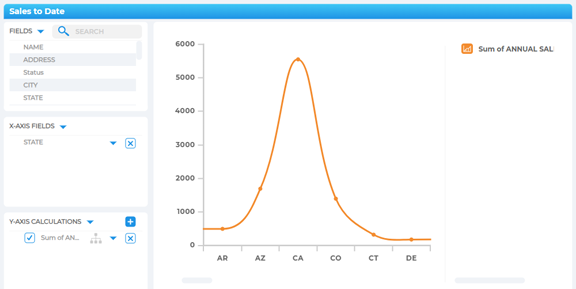
Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics tools use historical data, statistical models, and machine learning to forecast future outcomes. Common use cases include:
- Sales forecasting based on seasonality and pipeline trends
- Customer churn prediction using behavioral indicators
- Inventory optimization by anticipating future demand
These tools provide proactive visibility so teams can plan, prioritize, and pivot early.
Prescriptive Analytics Software
Prescriptive analytics software takes things a step further—by recommending (and sometimes automating) the best course of action based on predicted outcomes. It’s used in:
- Pricing optimization based on market elasticity
- Marketing campaign planning with suggested channel mix
- Supply chain routing to minimize cost and delivery time
While more complex, these tools close the gap between insight and action, making them valuable across high-stakes enterprise environments.
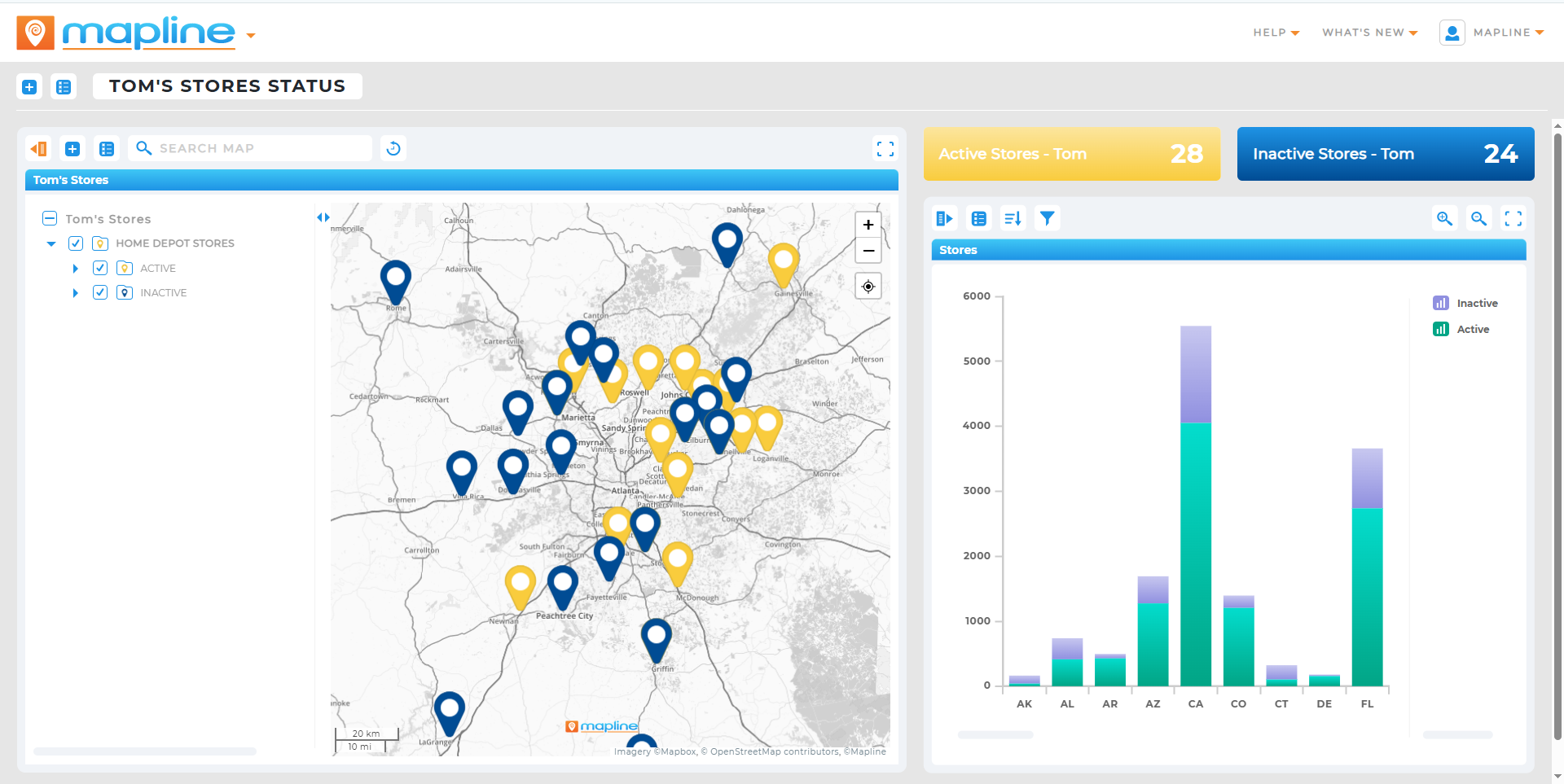
Machine Learning and AI-Powered Dashboards
AI has transformed the analytics landscape—especially in how data is visualized, interpreted, and acted upon. Machine learning analytics tools automate trend recognition and unlock dynamic modeling previously reserved for data scientists. These platforms continuously learn from incoming data, surfacing insights that evolve with your business. AI-powered dashboards simplify complex analytics by delivering real-time visualizations, alerts, and recommendations that non-technical users can act on immediately. As a result, teams can move faster, make smarter decisions, and adapt strategies based on real-time performance. From marketing to operations, AI dashboards make advanced analytics accessible and actionable.
AI-Powered Dashboards
AI-powered dashboards integrate machine learning to surface anomalies, suggest KPIs, and even generate plain-language summaries of key trends. Benefits include:
- Real-time trend detection without manual setup
- Automated alerts for significant data shifts
- Predictive visuals layered onto standard dashboards
These dashboards empower business users to make data-informed decisions—without waiting on analysts.
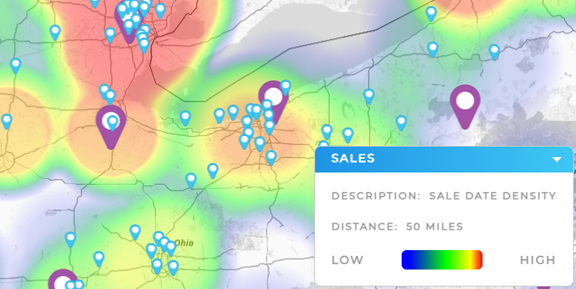
Anomaly Detection Tools
Anomaly detection tools use unsupervised learning to flag unusual patterns, such as:
- Spikes in web traffic or system performance
- Suspicious customer behavior or payment activity
- Operational disruptions before they escalate
Especially in finance, cybersecurity, and e-commerce, these tools protect revenue and brand reputation in real time.
Enterprise Data Science Tools and Big Data Platforms
Organizations working at scale require robust ecosystems for modeling, transformation, and insight delivery. That’s where enterprise data science tools and big data platforms come into play.
| Tool Category | Core Capabilities |
|---|---|
| Enterprise Data Science Tools | Custom model creation, scripting (Python/R), feature engineering, ML deployment |
| Big Data Platforms | Processing massive volumes of structured and unstructured data at speed (e.g., Hadoop, Spark) |
These tools provide the horsepower and flexibility needed for advanced modeling across millions (or billions) of records, and are often integrated with enterprise data lakes or warehouses.
Advanced Use Cases: Behavior Modeling, Attribution, and Geo Forecasting
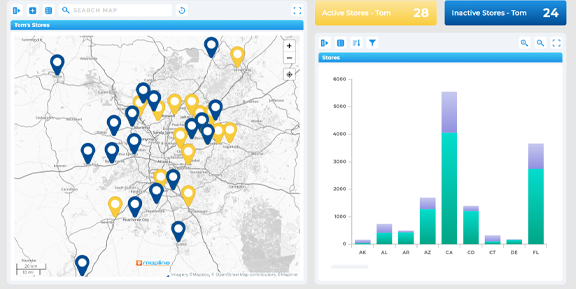
Once foundational tools are in place, advanced analytics can be applied to some of the most challenging (and rewarding) marketing and operational problems. Customer behavior modeling helps predict how different segments will respond to offers, content, or pricing—enabling hyper-personalized campaigns and smarter product decisions. Marketing attribution modeling clarifies which channels and touchpoints truly drive conversions, so teams can allocate budgets with confidence. Geo forecasting adds a spatial layer, allowing businesses to predict demand, identify regional trends, and plan market expansions with greater precision. These advanced use cases combine predictive power with strategic insight, helping organizations outmaneuver competitors and stay ahead of change.
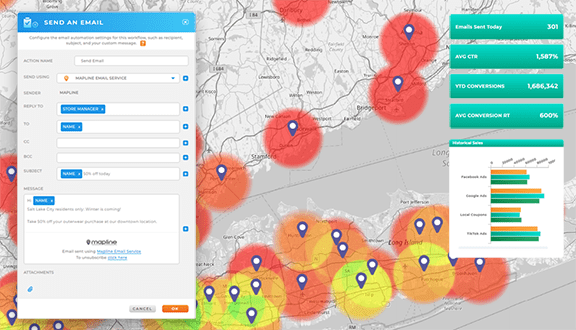
Customer Behavior Modeling
Customer behavior modeling helps marketers and product teams understand and predict user journeys—fueling personalization, conversion optimization, and retention strategy. Models may include:
- Purchase probability and timing
- Browsing-to-conversion funnel modeling
- Multi-touch customer journeys and abandonment points
These models help organizations deliver the right message at the right time—at scale.
Marketing Attribution Modeling
Marketing attribution modeling determines how credit for a sale or conversion is assigned across channels and touchpoints. Advanced models (like algorithmic or data-driven attribution) use statistical analysis to:
- Weigh the influence of each interaction
- Reveal hidden value in upper-funnel campaigns
- Guide smarter budget allocation across the media mix
When paired with machine learning, these models become more accurate over time, helping marketing teams maximize return on investment.
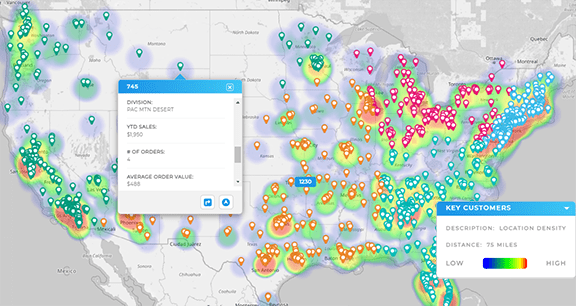
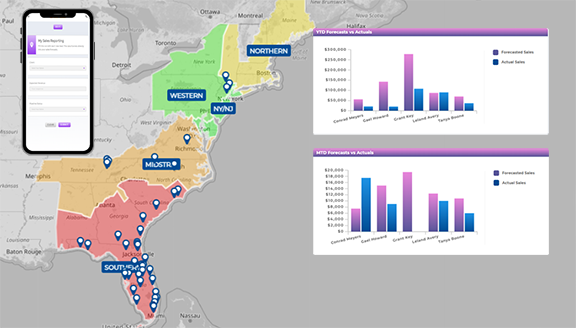
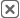
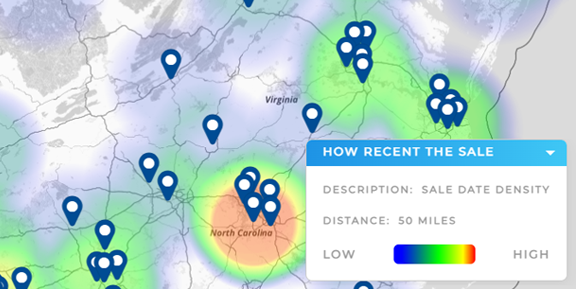
Geo Forecasting Tools and Spatial AI Insights
Geo forecasting tools and spatial AI insights bring location into the equation. These tools are critical for companies with regional operations or physical footprints. They can:
- Forecast demand by region, ZIP code, or store
- Model logistics and distribution efficiency
- Visualize spatial patterns in customer behavior
Adding the spatial dimension helps teams go from broad trends to highly localized insight—essential for franchise networks, retail chains, and last-mile delivery optimization.
Predictive analytics forecasts what is likely to happen based on data patterns. Prescriptive analytics recommends actions based on those predictions, often using optimization algorithms.
Not necessarily. Many platforms now offer self-service tools and AI-powered dashboards that non-technical teams can use. However, custom modeling often benefits from having data scientists involved.
Anomaly detection is widely used in fraud prevention, operational monitoring, system reliability, and campaign performance to flag unexpected changes.
Spatial AI combines geospatial data with machine learning to recognize patterns, forecast region-based behavior, and optimize location-based decisions at scale.
Virtually all industries benefit—especially finance, healthcare, logistics, retail, and marketing. Any business with large datasets and complex decisions can see ROI from advanced analytics.
While Mapline does not currently use artificial intelligence (AI) in the strictest technical sense, we leverage machine learning (ML) to power key capabilities—particularly in routing and spatial analysis.
Yes! All of the advanced analytics use cases described above can be achieved through our native Geo BI features, Mapline Data formulas, or via integrations with external tools. For more complex workflows like attribution modeling, behavior prediction, or anomaly detection, Mapline offers flexible ways to visualize insights and automate decisions—without requiring code or a data science background.