In an increasingly data-driven world, staying competitive means staying ahead—and advanced analytics makes that possible. Businesses that harness predictive modeling, diagnostic tools, and machine learning are better equipped to anticipate change, minimize risk, and make smarter decisions faster. Whether you’re forecasting sales, evaluating campaign performance, or optimizing operations, advanced analytics turns complex data into a strategic advantage. In this post, we’ll explore the core concepts of advanced analytics and how to apply them across your organization to drive scalable, future-ready growth.
What Is Advanced Analytics?
Advanced analytics goes beyond basic reporting and descriptive statistics. It includes predictive analytics, diagnostic analysis, data mining, machine learning, and forecasting—all with the goal of revealing patterns, identifying causes, and projecting future outcomes. Unlike traditional analytics, which focuses on “what happened,” advanced analytics answers “why” and “what’s next.” This approach empowers businesses to anticipate changes before they happen and proactively adapt to market trends, customer needs, and operational challenges.

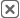
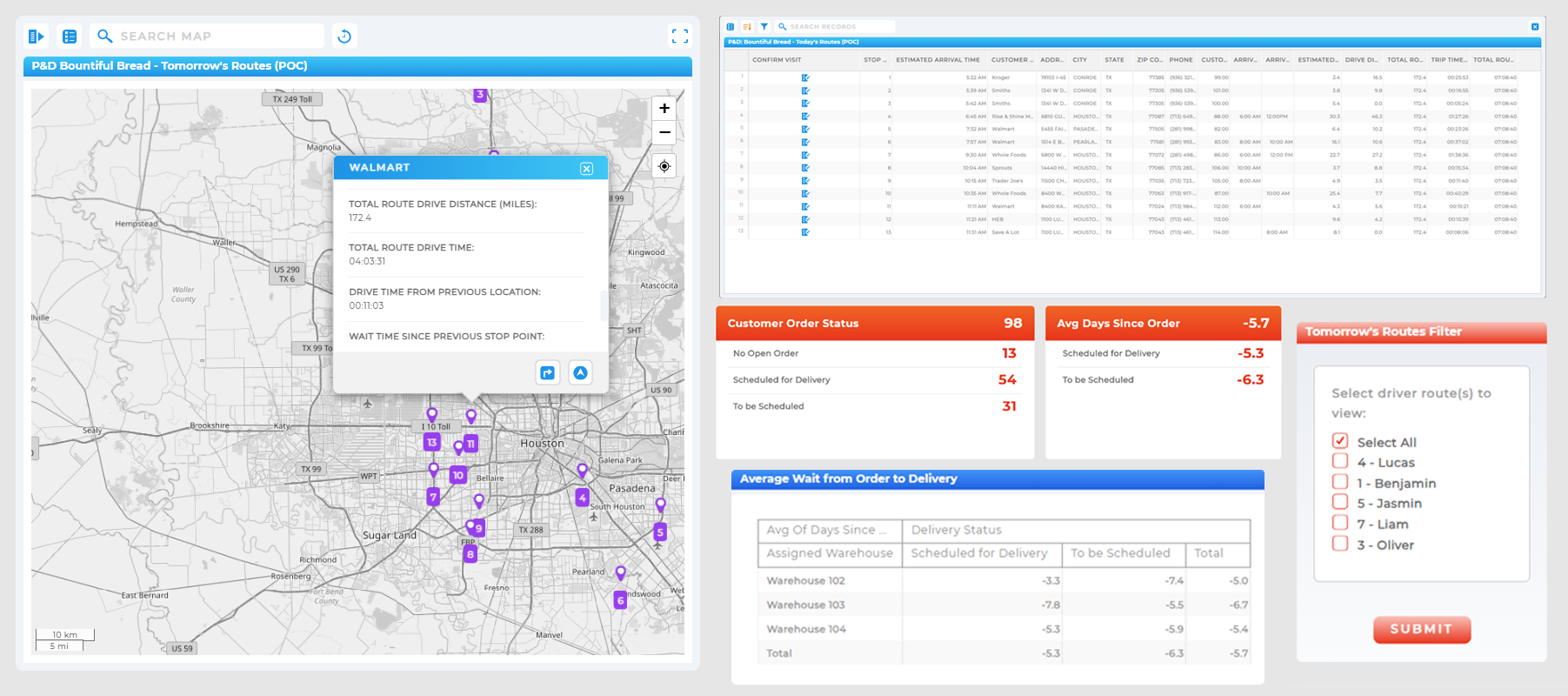
Pro Tip: Use Mapline’s advanced Geo Mapping features to layer business data with demographic and location intelligence. Forecast outcomes, evaluate market potential, and uncover untapped opportunities—powered by spatial data.
Types of Advanced Analytics Techniques
Advanced analytics encompasses several distinct methodologies, each designed to serve a specific purpose within a business. Whether you’re identifying future trends, diagnosing root causes of issues, or determining the best course of action, there’s a technique tailored for the job. Predictive models help anticipate customer behavior or market demand, while diagnostic tools dig into the why behind performance fluctuations. Prescriptive analytics offers strategic recommendations based on simulations and optimization models, and real-time analytics empowers teams to respond instantly as new data flows in.
These approaches work together to provide a comprehensive, forward-looking view of your business landscape. Understanding when and how to use each technique is key to maximizing the value of your data.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future trends. This is widely used in sales forecasting, customer behavior analysis, and risk management. With machine learning models, businesses can predict purchasing patterns, identify at-risk customers, and prepare for demand fluctuations.
Descriptive Analytics
Where descriptive analytics shows you what happened, diagnostic analytics helps you understand why it happened. It involves digging deeper into anomalies or performance dips to find root causes. This is essential for improving processes and fixing bottlenecks before they escalate.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes one step further by recommending the best course of action based on data models. It combines predictive analytics with business rules, simulations, and optimization algorithms to help teams make informed, timely decisions.
Real-Time Analytics
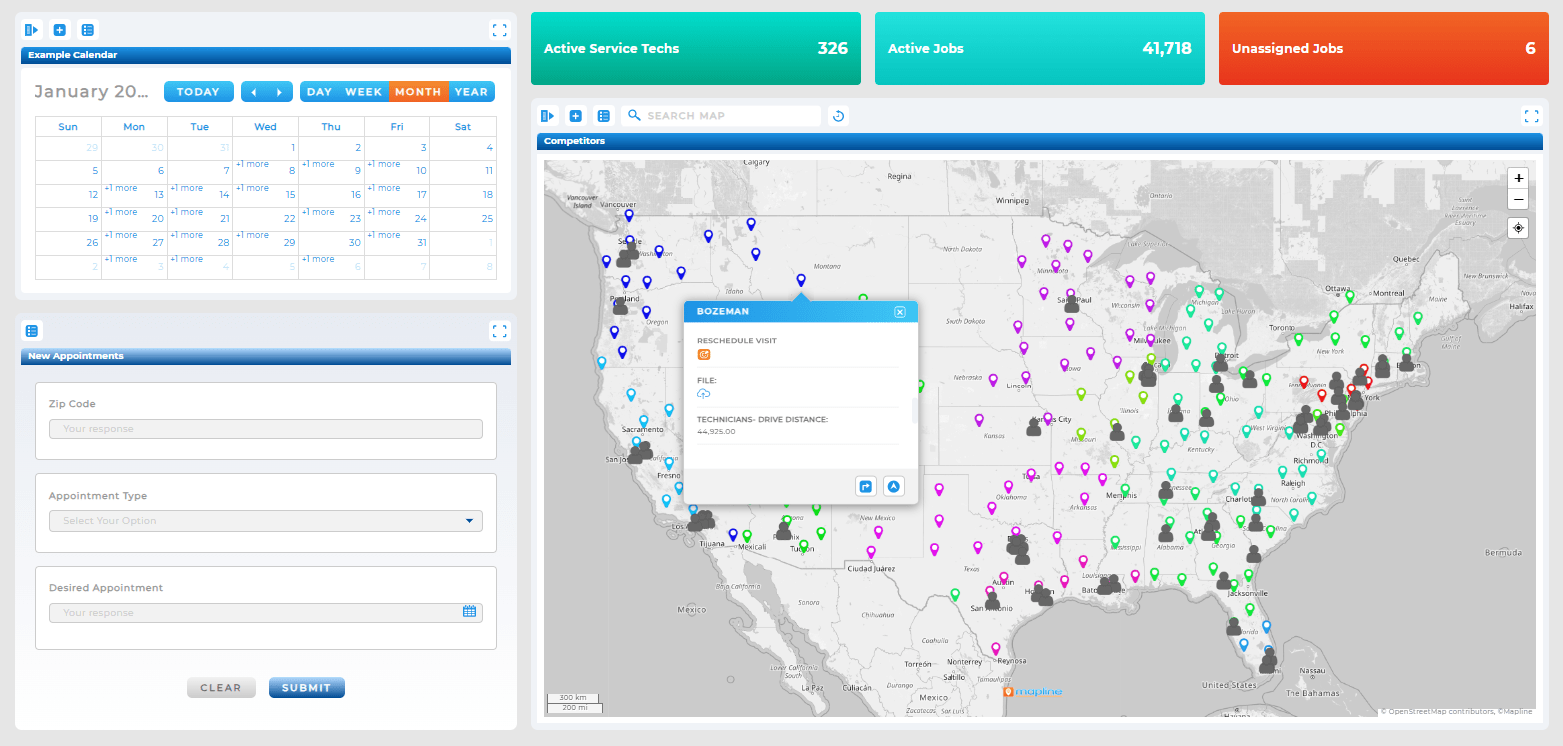
With real-time analytics, businesses can process and react to data as it’s collected. This is vital for industries like logistics, retail, and customer service, where immediate decisions can significantly impact performance and satisfaction.
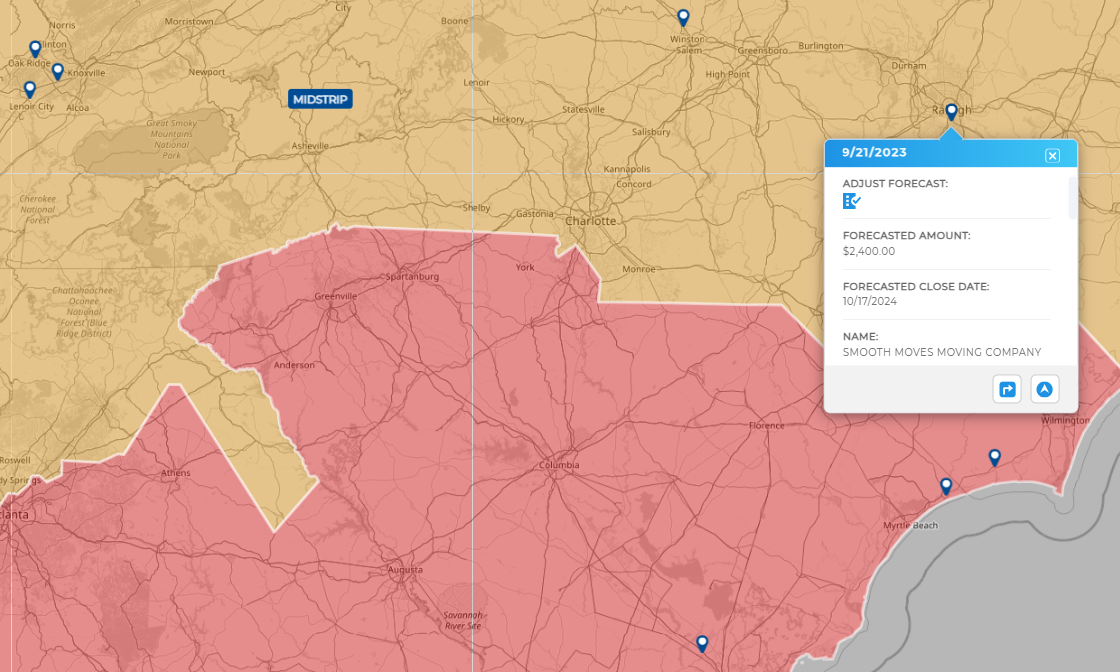
Business Use Cases for Advanced Analytics
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
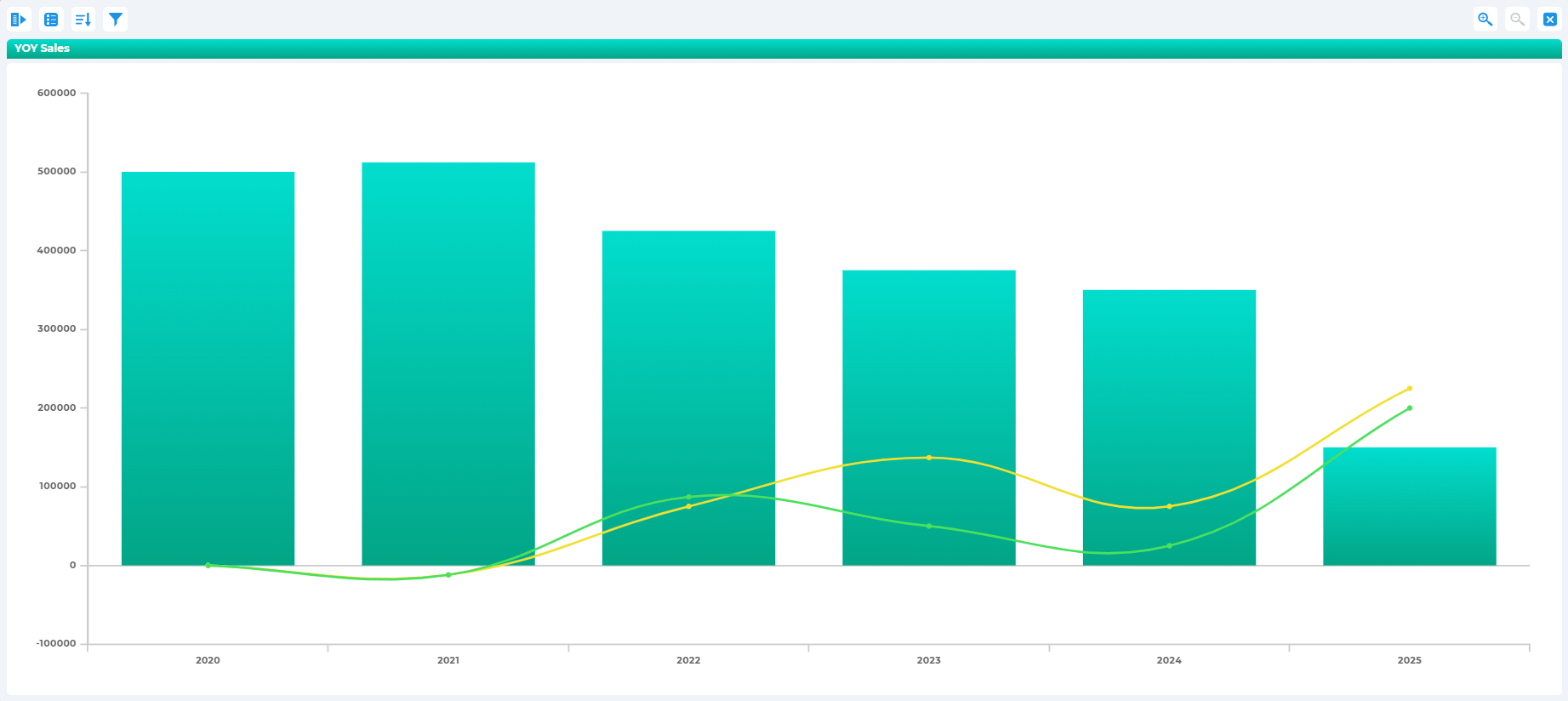
Financial Planning and Forecasting
Finance teams rely on forecasting models to evaluate cash flow trends, estimate revenue, and manage budget allocations. Advanced analytics helps reduce uncertainty by modeling best- and worst-case scenarios for upcoming quarters.
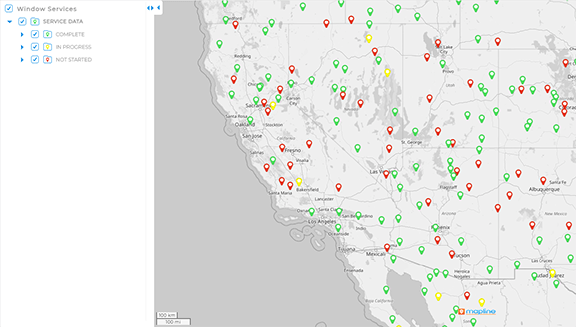
Operational Efficiency
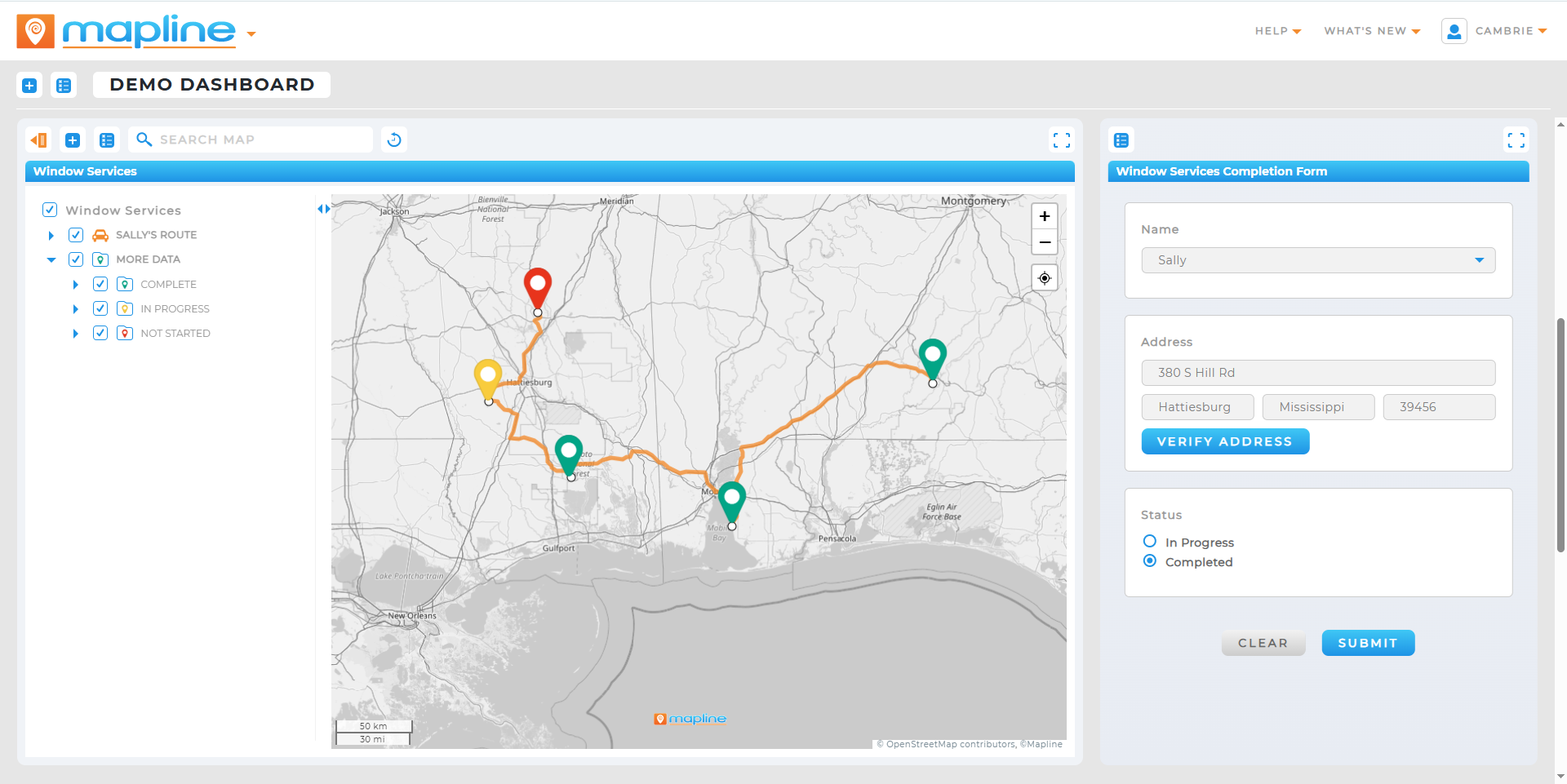
From warehouse automation to employee scheduling, analytics tools help teams pinpoint inefficiencies and design better workflows. Real-time data tracking also enables proactive maintenance and resource planning.
Customer Experience Optimization
Understanding customer behavior is critical to delivering better service. Diagnostic and behavioral analytics reveal pain points, churn risks, and areas for improvement—enabling businesses to tailor experiences and increase retention.
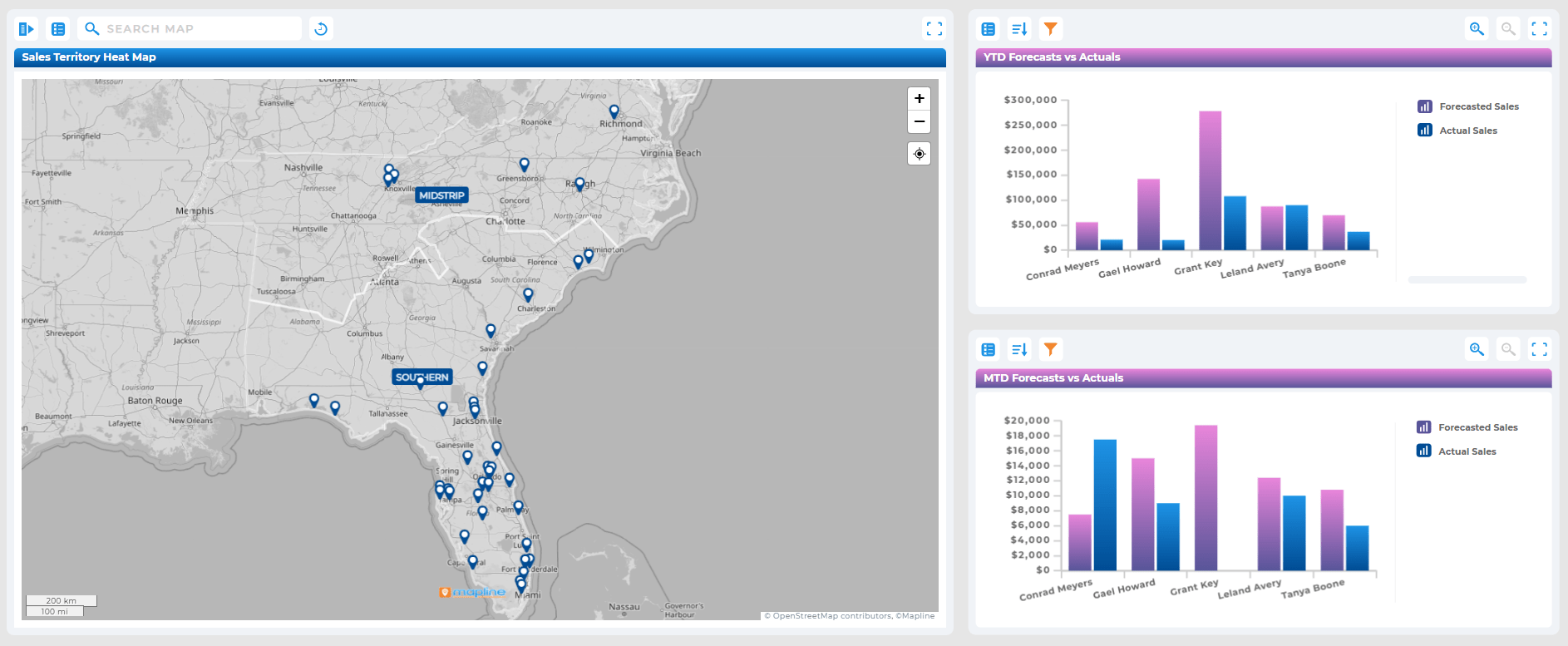
Predictive Marketing and Sales
Marketers use predictive analytics to identify high-value leads, determine optimal campaign timing, and personalize outreach. Sales teams can better allocate resources, optimize territories, and forecast revenue with increased accuracy.
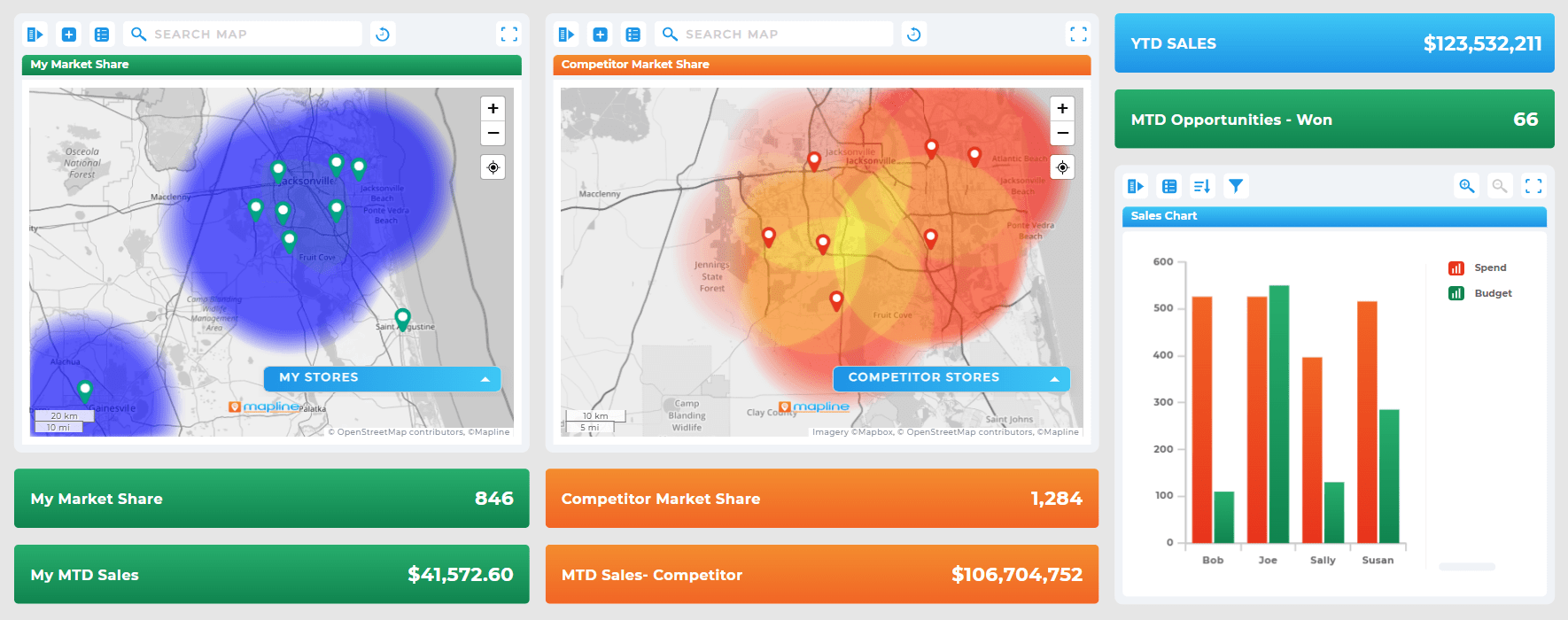
Benefits of Future-Proofing With Advanced Analytics
Adopting advanced analytics not only improves decision-making—it prepares your business to thrive under pressure. Here’s how it supports long-term success:
- Faster decision-making: Insights are delivered in real-time or near real-time, giving you the ability to act immediately.
- Improved risk mitigation: Forecast potential disruptions or downturns and prepare proactively.
- Better customer alignment: Analyze behavior and preferences to provide personalized, timely services.
- Increased operational resilience: Identify inefficiencies early and improve performance at every level.
The Future Is Already Here
Advanced analytics isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s the difference between businesses that adapt and those that fall behind. By implementing the right tools and techniques today, you position your organization to weather change, stay ahead of trends, and maximize impact at every level. Whether you’re just getting started or scaling up your data strategy, advanced analytics lays the foundation for a smarter, more resilient future.
Basic analytics provides summary statistics and trends, while advanced analytics uses modeling, machine learning, and forecasting to predict outcomes and recommend actions.
Machine learning helps uncover hidden patterns in large datasets and automates decisions—ideal for tasks like fraud detection, churn prediction, or inventory forecasting.
While data scientists can build custom models, many platforms—like Mapline—offer advanced analytics features in a user-friendly interface, making them accessible for non-technical users.
Accuracy depends on the quality and volume of your data, the modeling technique used, and how regularly your models are updated. With the right tools, predictive models can significantly outperform gut-based decisions.