- Blog
- Geo Mapping
- Best Sales Mapping Software in 2026: What Top Sales Teams Use (And Why)
Sales teams are operating in a far more complex environment than they were even a few years ago. Territories shift faster, buyer behavior is less predictable, and teams are expected to do more with fewer resources. In this landscape, sales mapping is no longer a “nice to have.” It has become a core operational capability that directly impacts revenue, productivity, and customer experience.
Teams that lack geographic intelligence struggle to see where opportunities cluster, where coverage breaks down, and how routes and territories affect performance. Static maps and spreadsheets can’t keep up with live data, growing datasets, or changing market conditions. As a result, many organizations leave revenue on the table without realizing it. Modern sales mapping software fills that gap by transforming location data into actionable insight.
Today’s top sales teams rely on platforms built for scale, speed, and adaptability—not legacy tools designed for one-time planning exercises. The best solutions support continuous optimization across territories, routes, and performance metrics. That shift is what separates high-growth sales organizations from those constantly playing catch-up.
What Sales Mapping Software Should Do in 2026
The bar for sales mapping software has risen significantly. Tools that once focused only on plotting locations or coloring territories now fall short of real operational needs. Modern sales teams require platforms that integrate data, geography, and analytics into a single, responsive system.
At a minimum, sales mapping software should visualize thousands—or even millions—of locations without performance issues. It must support dynamic territories that update as data changes, rather than forcing teams into manual redraws. Routing should reflect real sales constraints, including time windows, rep assignments, priorities, and regional coverage. Most importantly, maps should work alongside charts, KPIs, and reports to provide a complete operational view.
Scalability and adaptability are no longer optional. As sales conditions change, maps, territories, and insights must update in real time. Platforms that can’t evolve with the business quickly become bottlenecks instead of assets.

Pro Tip: If a sales mapping tool can’t grow with your data, territories, and routing needs, it’s not a long-term solution—it’s a temporary fix that will cost you more later.
What to Look For in Sales Mapping Software
The best sales mapping software does more than display data—it drives smarter execution. As sales teams grow, their tools must support larger datasets, dynamic territories, and increasingly complex workflows. Platforms that fall short in these areas often create bottlenecks instead of clarity. Evaluating sales mapping software requires a focus on scalability, intelligence, and adaptability. The following capabilities define what high-performing sales teams look for in 2026.
Unlimited Location & Data Scalability
Many sales mapping tools work well at a small scale but impose limits as datasets grow. Pin caps, row limits, and restricted uploads quietly restrict long-term growth. These constraints force teams into fragmented workflows, multiple maps, or manual workarounds that reduce visibility.
High-performing sales organizations need software built to handle enterprise-scale data without degradation. Platforms designed for large, complex datasets allow teams to grow without replatforming or compromising insight.
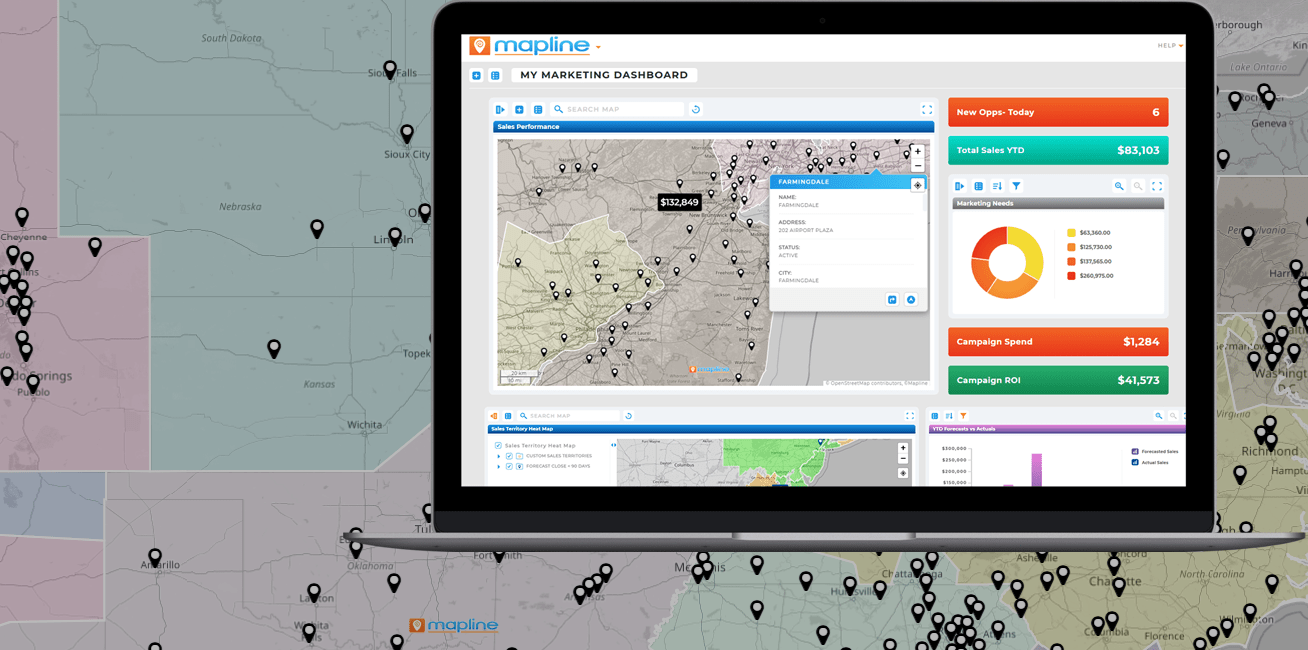
Territory Intelligence (Not Just Drawing Tools)
Drawing territories manually may work temporarily, but it doesn’t scale and rarely reflects real performance. ZIP-only or static territory tools fail to account for workload balance, demand shifts, or coverage gaps. Over time, this leads to uneven rep assignments and missed opportunities.
Territory intelligence goes beyond drawing shapes. It enables territories to respond to performance data, customer density, and regional demand—helping sales leaders maintain balance and fairness while maximizing coverage.
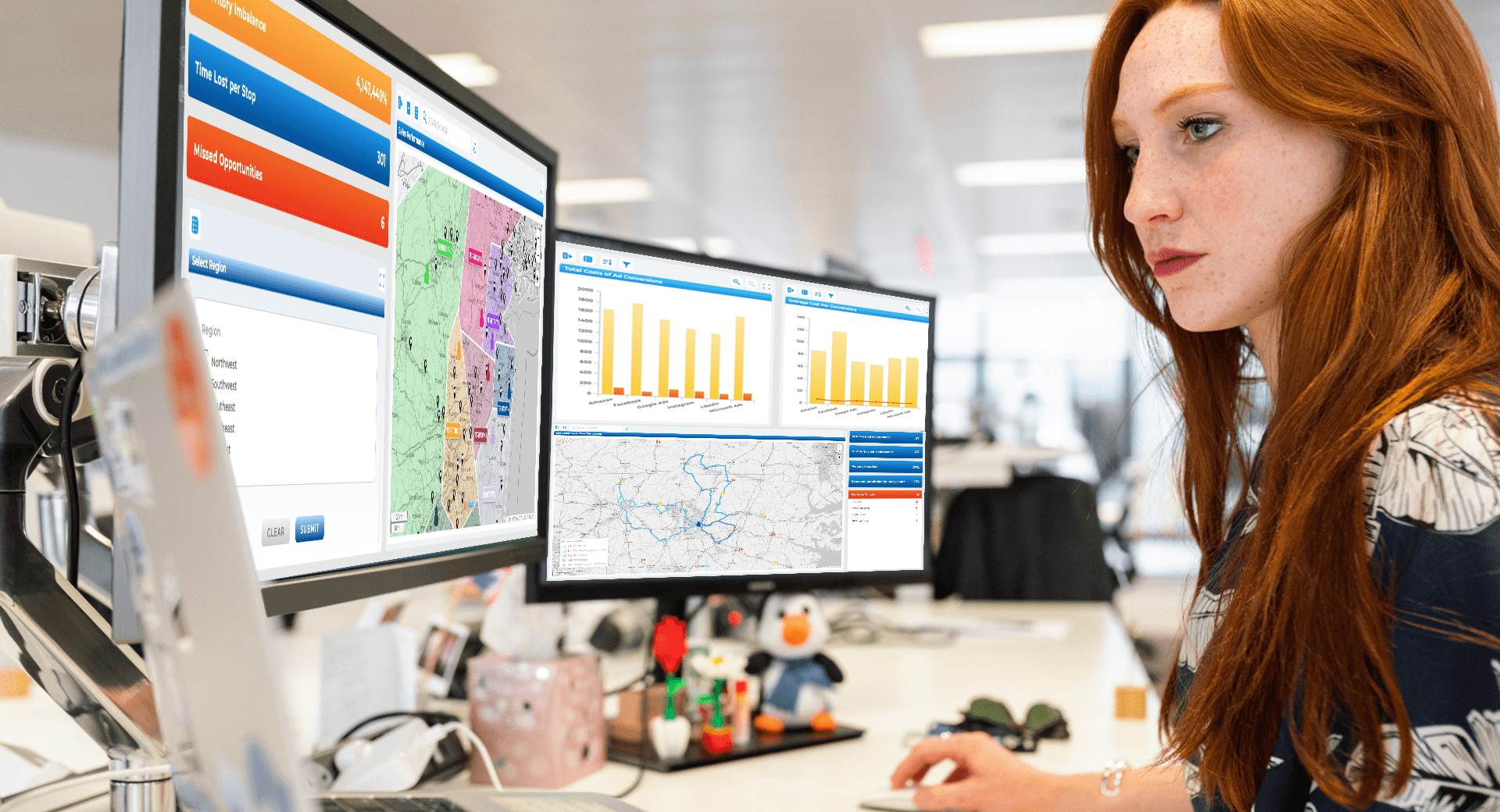

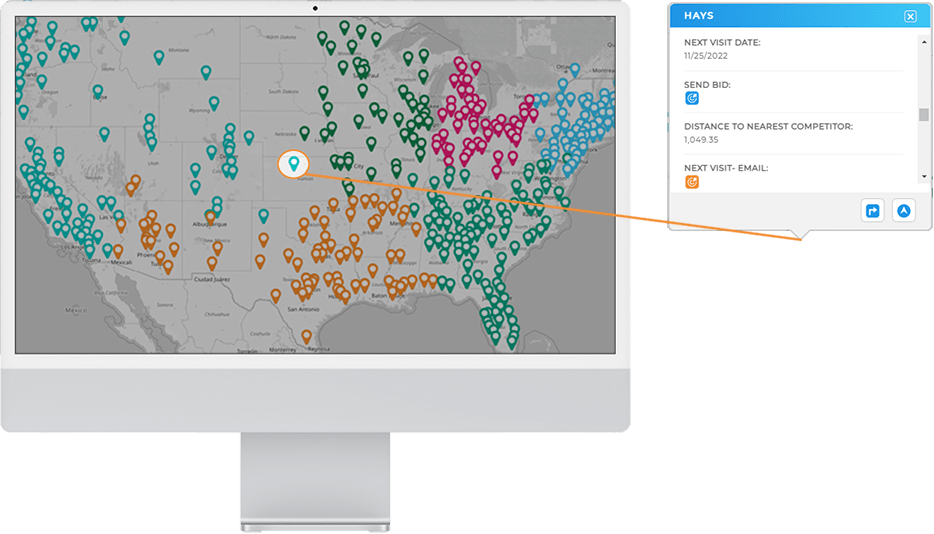
Advanced Routing for Real Sales Workflows
Sales routing is fundamentally different from delivery routing. Sales reps operate under unique constraints such as meeting windows, territory ownership, account priority, and flexible schedules. Tools built primarily for deliveries often struggle to support these realities.
Modern sales routing software must handle complex, real-world constraints without artificial stop limits or rigid assumptions. The ability to optimize routes dynamically allows reps to spend more time selling and less time driving.
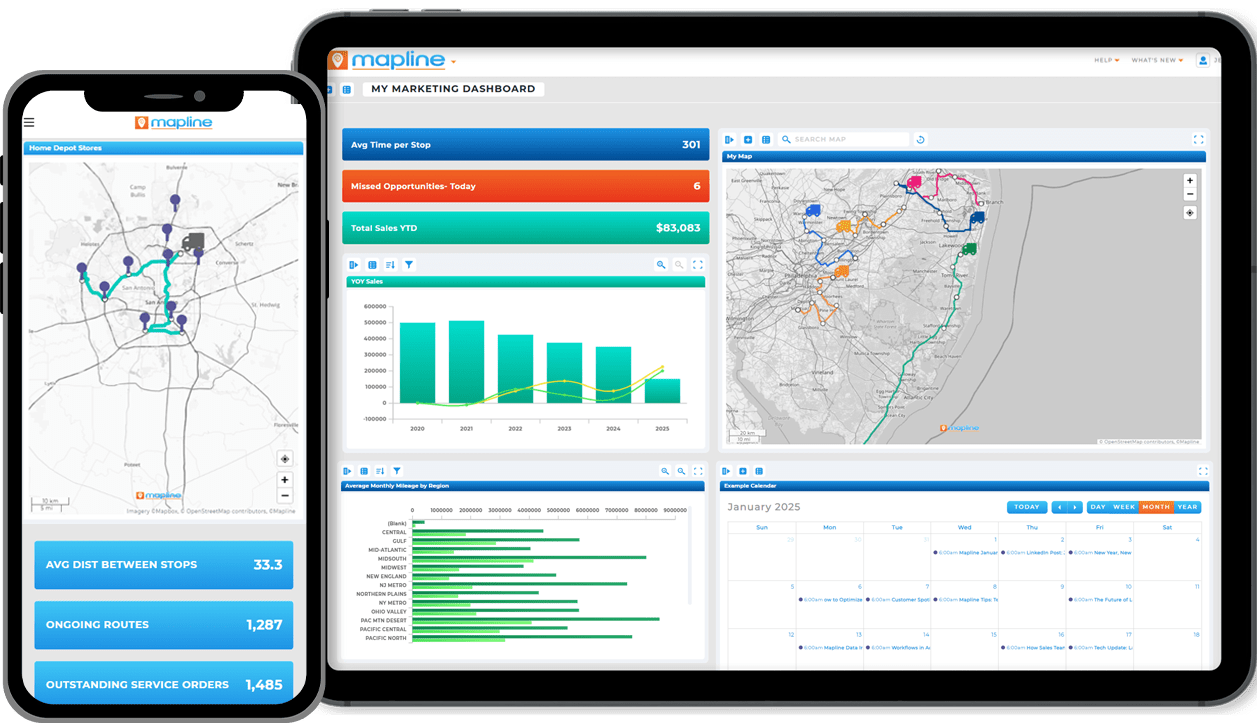
Built-In Geo BI & Analytics
When maps and analytics live in separate systems, teams lose momentum. Exporting data into external BI tools slows decisions and increases the risk of working from outdated information. Static screenshots replace live insight.
Built-in Geo BI eliminates this friction. By combining maps, dashboards, KPIs, and reports in one platform, sales leaders gain immediate visibility into what’s happening—and why.

Real-Time Adaptability
Monthly or quarterly territory planning no longer reflects how sales organizations operate. Market conditions change daily, sometimes hourly. Software that updates only on a schedule creates blind spots.
Real-time adaptability ensures maps, territories, and performance views update as data changes. This allows teams to adjust coverage, rebalance workloads, and respond to opportunity shifts without delay.
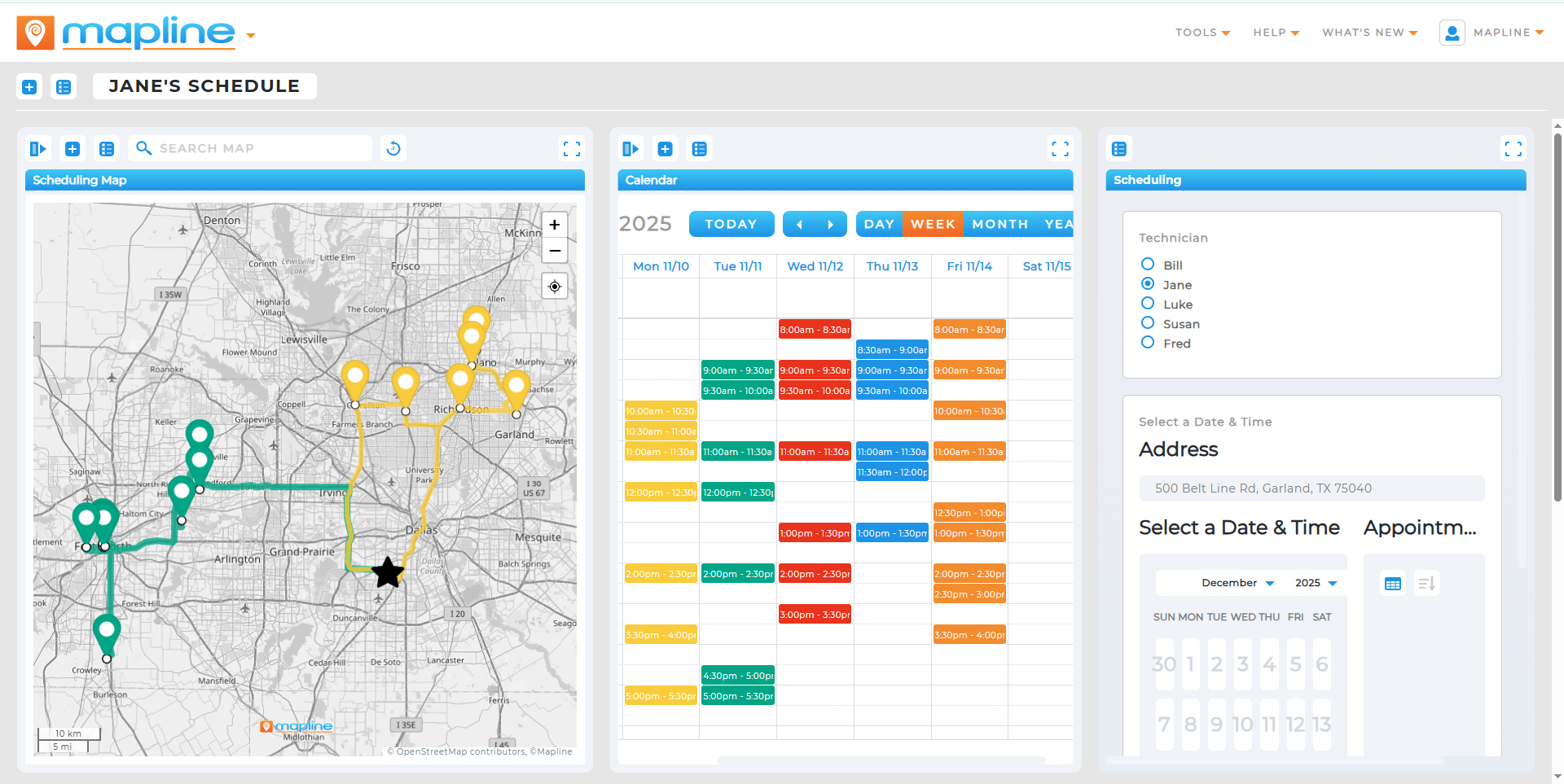
What to Avoid in Sales Mapping Software
Not every sales mapping solution is built with growth in mind. Some platforms prioritize simplicity at the expense of flexibility, while others lock teams into rigid workflows that can’t evolve. Over time, these tradeoffs create blind spots, inefficiencies, and operational friction. Recognizing these limitations early allows sales leaders to make more strategic technology decisions. Below are the most common pitfalls to watch for when evaluating sales mapping software.
Hard Limits on Locations, Routes, or Territories
Many sales mapping tools work well at a small scale, then quietly impose limits as your data grows. Caps on locations, routes, or territories force teams into awkward workarounds or multiple maps that fragment insight. These limits make long-term planning harder and slow teams down just as they start to scale. A modern sales mapping platform should grow with your data—not punish success.
Tools That Only Work Inside a CRM
CRM-native mapping tools can be useful early on, but they often lack flexibility outside the CRM environment. Sales operations don’t live entirely inside a single system—teams need visibility across datasets, regions, and workflows. When mapping tools are locked to CRM objects, analytics become constrained and customization becomes difficult. This limits how effectively sales leaders can plan territories, routes, and strategy.
Platforms Without Integrated Analytics
Some mapping tools focus solely on visualization, forcing teams to export data elsewhere for reporting. This disconnect slows decision-making and increases the risk of working from outdated information. Sales leaders need maps, metrics, and reports to update together in real time. Without built-in analytics, teams lose the ability to pivot quickly when performance shifts.
Routing Tools Built Only for Deliveries
Sales routing is fundamentally different from delivery routing. Many platforms optimize for drop-offs but fail to support real sales constraints like visit priorities, territory ownership, rep availability, or meeting windows. When routing tools don’t reflect how sales teams actually work, reps lose time and coverage suffers. A true sales mapping platform must support routing logic built for sales—not just logistics.
Limited Integrations or No Automation
Sales mapping tools without integrations or workflow automation can’t deliver real-time insight. If data updates require manual uploads or exports, maps and reports fall behind the moment operations change. This creates blind spots and delays that cost teams opportunities. Modern sales platforms should automatically sync data, update routes, refresh territories, and trigger workflows—without manual effort. Without automation, “real-time visibility” is just a promise, not a reality.


Pro Tip: If a platform can’t automatically update your maps, routes, and reports as your data changes, it’s not built for modern sales operations—no matter how polished the interface looks.
Best Sales Mapping Software Compared
As sales teams grow, the tools they rely on must shift from simple plotting utilities to comprehensive operational platforms. Too often, comparisons focus on bells and whistles rather than on whether a tool drives clarity, scale, and continuous improvement. The vendors below represent a diverse set of approaches to sales mapping—some strong in mobile workflows, others in territory design, and others suited to structured planning. By looking at each through a consistent, strategic lens, you’ll be better positioned to choose a solution that supports both your present needs and future growth. The sections that follow break down the practical strengths and limitations of each contender.
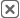
Mapline: Best Overall Sales Mapping Software
Mapline is built for sales teams that need scalability, flexibility, and real operational insight. It supports unlimited growth, intelligent territory design, advanced routing, and built-in Geo BI—all without requiring technical expertise.
Ideal for growing teams through enterprise sales operations, Mapline replaces multiple tools with a single, unified platform designed for real-world complexity.
Top Features & Strengths
- No-code map, territory, and routing configuration that sales ops teams can manage without engineering support
- Multi-dataset support that allows teams to layer customers, prospects, partners, and performance data together
- Role-based access controls that let leaders decide exactly who can view, edit, or share specific data
- Flexible sharing options, including view-only links, embedded maps, and internal collaboration workflows
- Native connectors and API support that allow Mapline to fit seamlessly into existing sales and ops tech stacks
- Visual styling controls for pins, territories, labels, and layers that improve clarity and executive readability
- Built-in demographic and government boundary layers that provide immediate market context without external tools
Why This Matters
Mapline is intentionally built for sales operations maturity. As teams grow more complex, the platform continues to support deeper workflows instead of forcing compromises.
Best used as:
A full-suite enterprise sales platform that manages the entire sales process end-to-end, minimizing spend and maximizing ROI.
Badger Maps: Best for Individual Rep Productivity
Badger Maps focuses on mobile-first experiences for individual reps. While effective for personal route planning, it can struggle with large datasets, advanced analytics, and enterprise-level territory intelligence.
Top Features & Strengths
- Strong mobile experience tailored to individual reps planning their own daily routes
- Offline access for reps working in areas with limited connectivity
- Mileage tracking and basic activity logging for rep-level reporting
- Simple CRM syncing that prioritizes ease of use over depth
Limitations:
- Territory planning and performance analysis require external tools
- Scaling beyond individual rep use cases becomes difficult
- Not designed for sales ops teams managing large or evolving datasets
Best used as:
A personal productivity tool for reps, not a system for sales planning or optimization.
SPOTIO: Focused on Door-to-Door Execution
SPOTIO excels in activity tracking and gamification for door-to-door teams. However, its mapping and analytics capabilities are more limited for broader sales operations.
Top Features & Strengths
- Built-in activity tracking for visits, calls, and outreach
- Gamification features that motivate high-volume field teams
- Lead generation via Google Places data
- Simple forms for structured data collection in the field
Limitations:
- Mapping serves activity tracking, not strategic analysis
- Geographic insight is limited compared to purpose-built mapping platforms
- Routing and territory workflows lack flexibility for non-door-to-door models
- Analytics focus more on rep behavior than market or territory performance
Best used as:
A sales engagement platform with mapping as a secondary capability.
eSpatial: Focused on Ad Hoc Territory Planning
eSpatial offers strong territory balancing tools. Its limitations appear when teams require advanced routing, real-time adaptability, or integrated analytics.
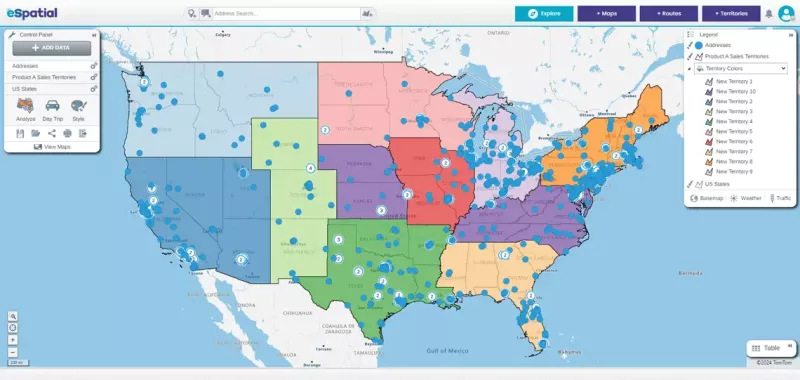
Top Features & Strengths
- Scenario comparison tools for evaluating different territory designs
- Weighted balancing models useful during realignment exercises
- Global territory support for international planning
- Export-friendly workflows for presentations and planning decks
Limitations:
- Built primarily for planning moments, not ongoing execution
- Less emphasis on continuous optimization or day-to-day sales workflows
- Routing and operational features are more limited
- Can feel rigid for teams that need to adapt frequently
Best used as:
A simple territory planning tool rather than a live sales operations platform.
Salesforce-Native Mapping Tools (e.g., Geopointe): CRM-Centric Mapping
Salesforce-native tools integrate directly into the CRM, which can be helpful early on. Over time, setup complexity, scalability limits, and reliance on Salesforce expertise can slow teams down.
Top Features & Strengths
- Deep integration with Salesforce objects and reports
- Ability to update CRM records directly from map views
- Familiar environment for Salesforce-first teams
- Works well for visualizing CRM data without leaving Salesforce
Limitations:
- Constrained by Salesforce data models and permissions
- Setup and customization often require Salesforce expertise
- Limited flexibility outside CRM-defined workflows
- Not well suited for cross-functional or multi-dataset analysis
Best viewed as:
A CRM visualization layer—not a standalone sales intelligence system.
Feature-By-Feature Comparison:
Best Sales Mapping Software of 2026
Before comparing platforms feature by feature, it’s important to understand what truly separates modern sales mapping software from tools that only scratch the surface. The most effective platforms don’t just visualize data; they support real sales execution at scale, adapt as conditions change, and connect planning with performance.
Mapline was built specifically to meet these demands. Instead of limiting teams as their data grows, Mapline provides a flexible, enterprise-grade foundation that supports continuous optimization across territories, routes, and analytics. The capabilities below represent the standard Mapline sets — and the bar against which other platforms should be measured. While many tools offer pieces of the puzzle, only a few are designed to support sales organizations end-to-end as they scale.
| Feature | Mapline | Badger Maps | SPOTIO | eSpatial | Salesforce-Native Mapping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unlimited locations | ✓ | ✖ Location caps | ✖ Volume limits | ⚠ Depends on plan | ✖ CRM object limits |
| Enterprise data scalability | ✓ | ⚠ Small-team focus | ⚠ Door-to-door scale | ⚠ Structured use only | ✖ Performance tied to CRM |
| Intelligent territory logic | ✓ | ✖ Manual only | ⚠ Basic assignment | ⚠ Planning-focused | ⚠ Rules-based only |
| Advanced sales routing | ✓ | ⚠ Rep-level routes | ⚠ Limited constraints | ⚠ Small route volume | ⚠ Add-on required |
| Built-in Geo BI dashboards | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ⚠ Limited analytics | ⚠ Salesforce reports only |
| Real-time adaptability | ✓ | ✖ Static updates | ⚠ Manual refresh | ⚠ Planning cycles | ⚠ CRM refresh delays |
| Multi-dataset layering | ✓ | ✖ Single dataset | ⚠ Limited objects | ⚠ Structured inputs | ⚠ Salesforce objects only |
| Role-based access controls | ✓ | ⚠ Limited roles | ⚠ Activity-based roles | ✓ | ✓ Salesforce roles |
| Native integrations & API | ✓ | ⚠ CRM-centric | ⚠ CRM-centric | ⚠ Limited automation | ⚠ Salesforce-only |
| Custom map & territory styling | ✓ | ⚠ Basic styling | ⚠ Limited visuals | ⚠ Planning-focused | ⚠ CRM map styles |
| Governance & data control | ✓ | ✖ | ⚠ Activity-level only | ✓ | ✓ Salesforce governance |
Why Mapline Is the #1 Sales Mapping Software for Growing Teams
Mapline connects sales planning, execution, and optimization in one system. Teams move seamlessly from territory design to routing, reporting, and ongoing performance improvement.
By replacing fragmented tools with a single platform, Mapline simplifies workflows and increases visibility. Its flexibility allows teams to adapt as markets change, while its scalability ensures it continues to perform as organizations grow.
How Sales Teams Use Mapline to Win More Deals
Sales teams use Mapline to optimize territories, ensuring balanced workloads and full market coverage. Smarter routing increases face time with customers while reducing wasted drive hours.
Market gaps become visible through geographic analysis, allowing teams to focus effort where opportunity is highest. Performance-based territory adjustments and Geo BI dashboards enable faster, more confident decisions.
How to Choose the Right Sales Mapping Software for Your Team
When evaluating vendors, teams should ask whether the platform can scale without limits, adapt in real time, and support both planning and execution. Red flags include rigid caps, disconnected analytics, and tools built for narrow use cases.
Future-proofing matters more than short-term pricing. A platform that grows with your data, territories, and routing needs delivers far greater ROI over time.
Sales mapping software helps teams visualize customers, territories, and routes geographically. It turns location data into actionable insight that improves coverage, planning, and execution.
By optimizing territories and routes, sales reps spend less time traveling and more time selling. Leaders gain visibility into performance and workload balance.
CRM mapping focuses on account visualization inside the CRM. Sales mapping platforms offer broader datasets, deeper analytics, routing, and territory intelligence beyond CRM objects.
Modern platforms are built to scale across thousands of users and locations. Scalability is a key differentiator between entry-level tools and enterprise solutions.
Advanced sales mapping software includes both. Routing and territory intelligence are essential for maximizing coverage and efficiency.
Geo BI combines analytics with geographic context, revealing trends, gaps, and opportunities that charts alone can’t show. It enables faster, more informed decisions.