- Blog
- Geo Mapping
- How Marketing Mapping Tools Turn Campaign Data Into Geographic Insight
Marketing data rarely fails because there isn’t enough of it. It fails because patterns are buried inside spreadsheets, dashboards, and disconnected tools that don’t show where performance is happening.
Marketing mapping tools solve this problem by adding geographic context to campaign data. Instead of reviewing metrics in isolation, teams can see how performance varies by region, territory, ZIP code, or market. This spatial perspective turns raw analytics into insight that’s easier to interpret and act on.
When used correctly, marketing mapping tools don’t just visualize data. They expose inefficiencies, reveal opportunity gaps, and help teams align strategy with real-world geography.
Why Geography Changes How Campaign Performance Is Interpreted
A campaign that looks average at a national level can be wildly uneven once mapped. Geography introduces context that traditional dashboards often miss, such as regional demand, market maturity, travel constraints, and competitive density.
By visualizing performance spatially, teams can distinguish between underperforming campaigns and underperforming markets. This distinction matters because the response is different. One requires creative or messaging changes, while the other may require territory realignment, budget shifts, or localized strategy.
Geographic insight helps marketing teams ask better questions earlier in the analysis process.


Pro Tip: Before mapping campaign results, normalize your data by geography first (ZIP code, territory, or region). When every campaign uses the same geographic structure, marketing mapping tools can reveal true performance patterns instead of misleading hotspots caused by inconsistent data.
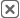
It Reveals Regional Performance Gaps Instantly
Marketing mapping tools make it obvious when certain regions outperform others. Instead of scanning rows of data, teams can immediately see clusters of high and low engagement, conversion, or revenue.
This makes it easier to identify where campaigns resonate and where they fall flat. It also helps avoid overcorrecting based on averages that hide regional variation.
It Separates Market Potential From Execution Issues
Poor results don’t always mean poor strategy. Some regions simply have lower demand, longer sales cycles, or heavier competition. Mapping campaign data alongside geographic boundaries helps teams determine whether performance issues are structural or fixable.
This prevents wasted spend trying to force growth in markets that aren’t ready while ignoring regions with untapped potential.
It Adds Context to Attribution and ROI
Attribution models improve when geography is part of the analysis. Mapping shows how channels perform differently across markets, revealing where certain tactics are more effective.
This geographic lens leads to smarter allocation decisions and more realistic ROI expectations by region.
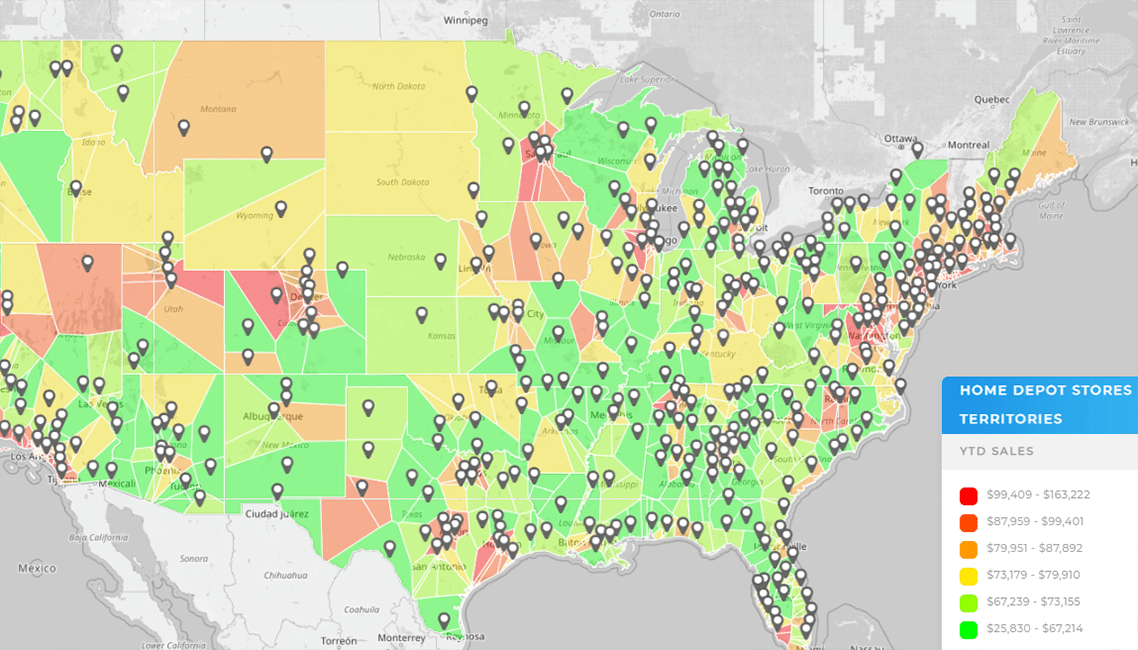
What Marketing Mapping Tools Actually Do
At their core, marketing mapping tools connect campaign data to location. This allows teams to visualize performance metrics on a map and interact with them dynamically.
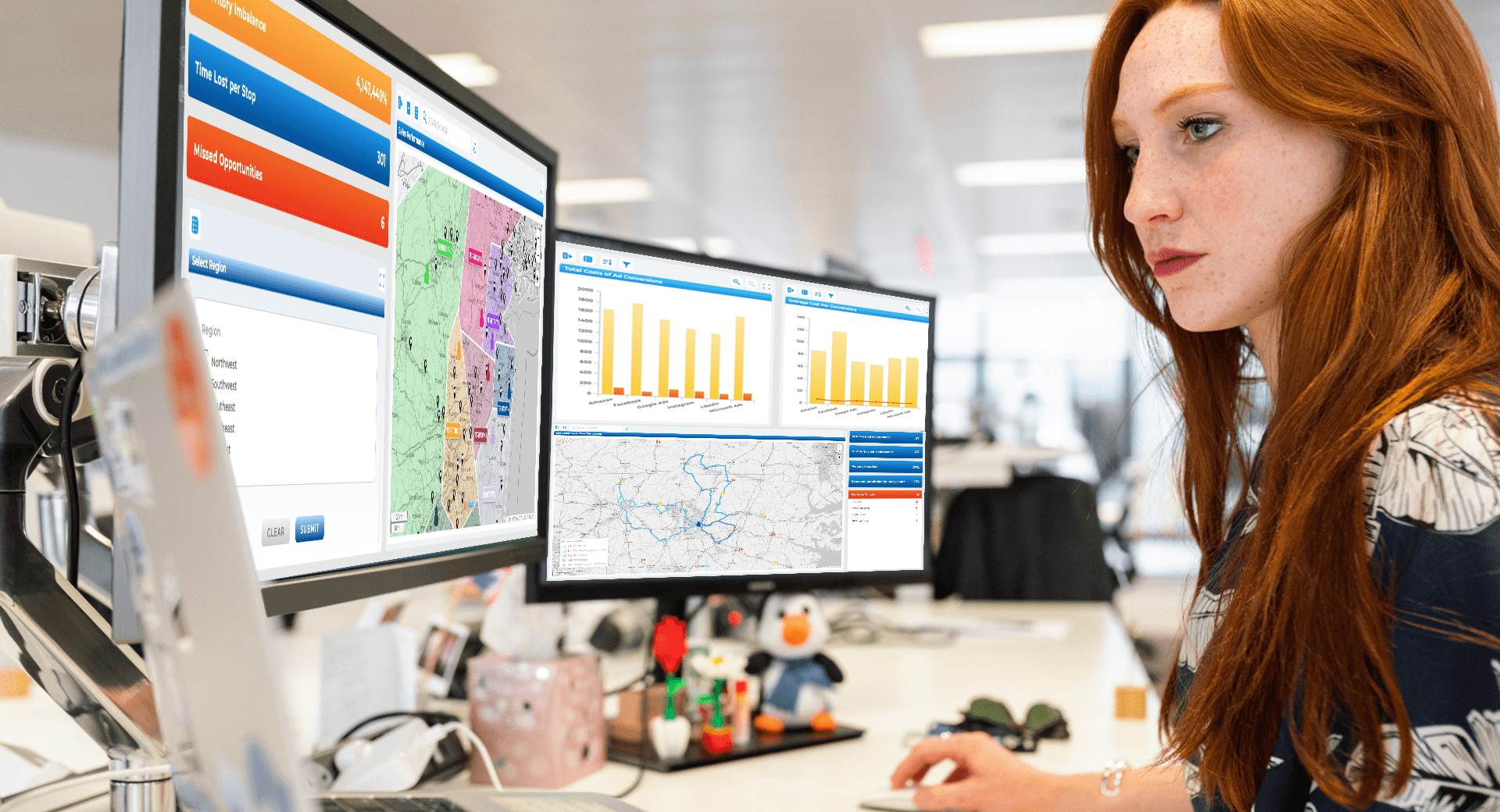
When paired with territory mapping, these tools help teams evaluate results within the context of defined markets, sales regions, or operational boundaries instead of arbitrary groupings.
Used correctly, mapping tools bridge the gap between analytics and execution.
They Turn Campaign Metrics Into Spatial Signals
Metrics like impressions, leads, conversions, and revenue take on new meaning when viewed geographically. Mapping highlights patterns that aren’t visible in charts or tables, such as regional saturation or uneven coverage.
This makes it easier to diagnose issues and prioritize action.
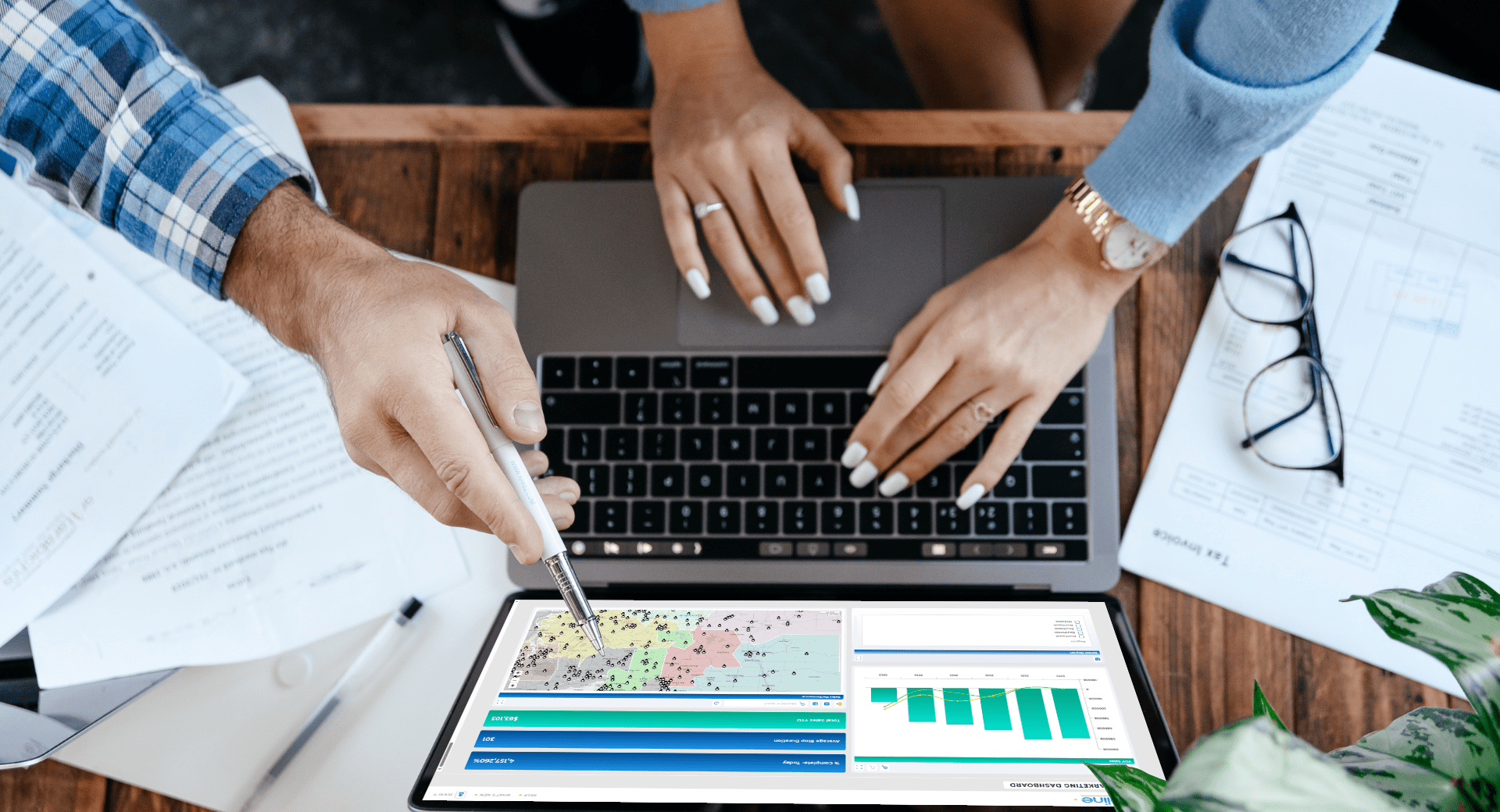

They Support Market and Competitive Analysis
Marketing mapping tools allow teams to overlay internal performance data with external signals like competitor presence, demographics, or market size. This creates a more complete picture of why certain regions perform differently.
It also supports more informed market assessment and expansion planning.
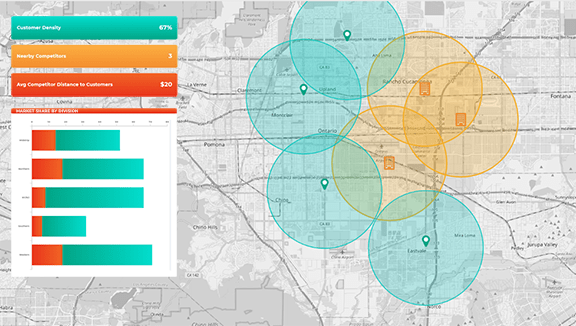
They Align Marketing and Sales Around Shared Geography
When marketing insights are mapped using the same geographic structures as sales teams, alignment improves. Campaign performance can be evaluated within the same territories sales operate in, reducing friction between teams.
This shared view makes collaboration easier and planning more realistic.
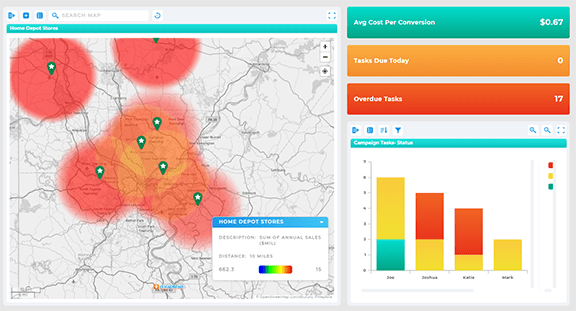
Turning Mapped Insights Into Action
Visualization alone isn’t enough. The value of marketing mapping tools comes from how easily insights translate into decisions.
When combined with mapping software and Geo Mapping, teams can filter, segment, and act on geographic insights without exporting data or rebuilding reports.
Reallocating Spend Based on Regional Performance
Mapped data makes it clear where additional budget is likely to produce returns and where spend should be reduced or paused. This allows teams to optimize campaigns continuously instead of waiting for post-mortem analysis.
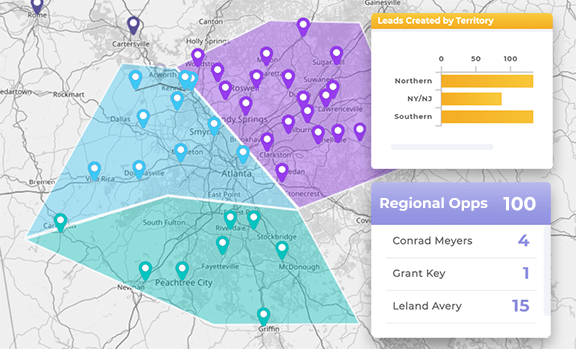
Refining Targeting and Messaging by Market
Geographic insight helps teams tailor messaging to local conditions. What works in one region may not work in another, and mapping highlights where customization is needed.
This improves relevance without increasing complexity.
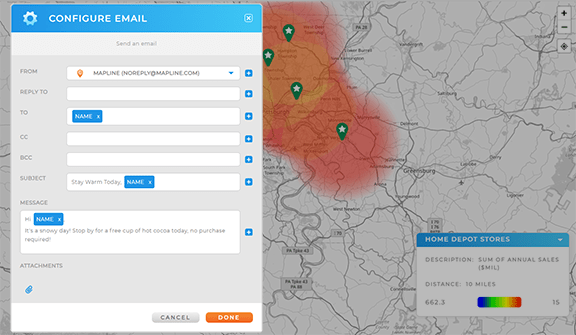
Supporting Long-Term Market Strategy
Over time, mapped campaign data becomes a strategic asset. Trends across regions help teams decide where to expand, where to defend share, and where to exit.
This turns marketing analytics into a long-term planning tool instead of a reactive reporting function.

Why Mapping Beats Traditional Marketing Analytics
Traditional dashboards are excellent at tracking metrics but weak at showing relationships. Mapping adds context that dashboards can’t.
By incorporating territory mapping, marketing mapping tools connect performance to real-world structure. This helps teams understand not just what happened, but why it happened and where to act next.
Marketing mapping tools visualize campaign and performance data on a map, allowing teams to analyze results by region, territory, or market instead of only through charts and tables.
Standard analytics tools focus on metrics over time. Marketing mapping tools add geographic context, making it easier to spot regional patterns and gaps.
Yes. By layering competitor locations or market data with campaign performance, teams can better understand competitive dynamics by region.
No. They complement dashboards by adding spatial insight that dashboards alone can’t provide.
Teams managing multi-region campaigns, distributed markets, or territory-based sales structures benefit the most from geographic insight.